Difference between revisions of "What to Do with Fabric"
Alessandro (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | =How to Dye Fabric / Textile with Natural Colors | + | =How to Dye Fabric / Textile with Natural Colors= |
| − | {{:How to Dye Fabric / Textile with Natural Colors | + | {{:How to Dye Fabric / Textile with Natural Colors}} |
| − | =How to Recycle Fabric | + | =How to Recycle Fabric= |
| − | {{:How to Recycle Fabric | + | {{:How to Recycle Fabric}} |
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Requested translation to Spanish]] [[Category:Requested translation to French]] | ||
Latest revision as of 17:26, 6 December 2009
Contents
- 1 How to Dye Fabric / Textile with Natural Colors
- 2 Natural Dyeing of Textiles - Technical Brief
- 2.1 Introduction
- 2.2 Types of textiles suitable for dying
- 2.3 Equipment needed for home dyeing and very small-scale commercial dyeing
- 2.4 Mordants
- 2.5 Natural dyestuffs
- 2.6 Testing dyes
- 2.7 The process of dyeing
- 2.8 References and further reading
- 2.9 Useful addresses
- 2.10 Useful internet addresses
- 2.11 Related articles
- 2.12 Categories
- 3 How to Recycle Fabric
How to Dye Fabric / Textile with Natural Colors
Natural Dyeing of Textiles - Technical Brief
Introduction
Dyeing is an ancient art which predates written records. It was practised during the Bronze age in Europe. Primitive dyeing techniques included sticking plants to fabric or rubbing crushed pigments into cloth. The methods became more sophisticated with time and techniques using natural dyes from crushed fruits, berries and other plants, which were boiled into the fabric and gave light and water fastness (resistance), were developed.
Some of the well known ancient dyes include madder, a red dye made from the roots of the Rubia tinctorum, blue indigo from the leaves of Indigofera tinctoria, yellow from the stigmas of the saffron plant, and dogwood, an extract of pulp of the dogwood tree. The first use of the blue dye, woad, beloved by the Ancient Britons, may have originated in Palestine where it was found growing wild. The most famous and highly prized colour through the age was Tyrian purple, noted in the Bible, a dye obtained from the spiny dye-murex shellfish. The Phoenicians prepared it until the seventh century, when Arab conquerors destroyed their dyeing installations in the Levant. A bright red called cochineal was obtained from an insect native to Mexico. All these produced high-quality dark colours. Until the mid-19th century all dyestuffs were made from natural materials, mainly vegetable and animal matter.
Today, dyeing is a complex, specialised science. Nearly all dyestuffs are now produced from synthetic compounds. This means that costs have been greatly reduced and certain application and wear characteristics have been greatly enhanced. But many practitioners of the craft of natural dying (i.e. using naturally occurring sources of dye) maintain that natural dyes have a far superior aesthetic quality which is much more pleasing to the eye. On the other hand, many commercial practitioners feel that natural dyes are non-viable on grounds of both quality and economics. In the West, natural dyeing is now practised only as a handcraft, synthetic dyes being used in all commercial applications. Some craft spinners, weavers, and knitters use natural dyes as a particular feature of their work.
In many of the world’s developing countries, however, natural dyes can offer not only a rich and varied source of dyestuff, but also the possibility of an income through sustainable harvest and sale of these dye plants. Many dyes are available from tree waste or can be easily grown in market gardens. In areas where synthetic dyes, mordants (fixatives) and other additives are imported and therefore relatively expensive, natural dyes can offer an attractive alternative.
The knowledge required for sourcing and extracting such dyes and mordants is, however, often not available as extensive research work is required to identify suitable plants, minerals, etc. In Zambia for example, there is a wealth of plants available for producing natural dyes, but due to lack of knowledge of the processes involved in harvesting and processing the plants, little use is made of this natural resource. In some countries, such as India, Nigeria and Liberia, where this research has been carried out, or where there exists a tradition of natural dyeing, natural dyes and mordants are used widely.
</div>
Types of textiles suitable for dying
Natural dyes can be used on most types of material or fibre but the level of success in terms of fastness and clarity of colour varies considerably. Users of natural dyes, however, tend to also use natural fibres, and so we will look in more detail at this group. Natural fibres come mainly from two distinct origins, animal origin or vegetable origin. Fibres from an animal origin include wool, silk, mohair and alpaca, as well as some others which are less well known. All animal fibres are based on proteins. Natural dyes have a strong affinity to fibres of animal origin, especially wool, silk and mohair and the results with these fibres are usually good. Fibres of plant origin include cotton, flax or linen, ramie, jute, hemp and many others. Plant fibres have cellulose as their basic ingredient. Natural dyeing of certain plant based textiles can be less successful than their animal equivalent. Different mordanting techniques are called for with each category. When a blend of fibre of both animal and plant origin is being dyed, then a recipe should be chosen which will accentuate the fibre which is required to be dominant.
Equipment needed for home dyeing and very small-scale commercial dyeing
Most equipment needed for dyeing fabrics at home, or at the very small-scale commercial level, can be found in almost any market place throughout the world. The following is a list of the equipment requirements and a brief explanation of their use.
- Heat source. This can be any type of cooking stove; gas, wood, kerosene, charcoal, electricity. This is used for heating the liquid used during mordanting and dyeing.
- Pestle and mortar. Used for milling the natural dye or minerals, where this is called for.
- Mordanting and dyeing pans. Stainless steel or enamel pans are the most suitable for dyeing. The size of pan depends upon the quantities of fabric that will be dyed. Do not use pans made from copper, aluminium or iron, unless absolutely necessary, as these metals have properties which can change the colour of the dye.
- tirring rods. Stainless steel or glass rods are best as they can be cleaned and used for different colour dyes. If wooden stirring rods are used then there should be a different spoon for each colour.
- Thermometer. This is used to measure the temperature of the liquid during mordanting and dyeing. A long thermometer (to reach the liquid at the bottom of the pan) is preferred, with a range of 0 - 100oC (32 - 210oF).
- Measuring jugs. These are used to measure the quantities of liquid called for in the recipe. Sometimes precise quantities are called for.
- Storage containers. Used for storing the dyestuffs and mordants. Large glass and plastic jars are ideal. Some mordants and dyes are sensitive to light and should therefore be stored in sealed light-proof containers.
- Plastic bowls and buckets. A variety of plastic bowls or buckets of varying sizes are useful when wetting or rinsing fabrics.
- Strainer. Used for straining the liquid off the dyestuff in the dyebath.
- Weighing scales. Used for obtaining the correct quantities as specified in the recipe. A scales with metric and imperial measurement is useful as conversions from one system to the other are not then needed.
- Protective equipment. Gloves for holding hot pans will prevent burns. An apron will protect your clothing. Rubber gloves will prevent skin irritation caused by mordants, and will also prevent you from dyeing your hands. A face mask can cut down the amount of fumes or powder inhaled during the dyeing process.
Mordants
Few natural dyes are colour-fast with fibres. Mordants are substances which are used to fix a dye to the fibres. They also improve the take-up quality of the fabric and help improve colour and light-fastness. The term is derived from the Latin mordere, to bite. Some natural dyes, indigo for example, will fix without the aid of a mordant; these dyes are known as ‘substantive dyes’. Others dyes, such as madder and weld, have a limited fastness and the colour will fade with washing and exposure to light. Traditionally, mordants were found in nature. Wood ash or stale urine may have been used as an alkali mordant, and acids could be found in acidic fruits or rhubarb leaves (which contain oxalic acid), for example. Nowadays most natural dyers use chemical mordants such as alum, copper sulphate, iron or chrome (there are concerns, however about the toxic nature of chrome and some practitioners recommend that it is not used).
Mordants are prepared in solution, often with the addition of an ‘assistant’ which improves the fixing of the mordant to the yarn or fibre. The most commonly used mordant is alum, which is usually used with cream of tartar as an additive or assistant. Other mordants are:
- Iron (ferrous sulphate)
- Tin (stannous chloride)
- Chrome (bichromate of potash)
- Copper sulphate
- Tannic acid
- Oxalic acid
Using a different mordant with the same dyestuff can produce different shades, for example;
- Iron is used as a ‘saddener’ and is used to darken colours.
- Copper sulphate also darkens but can give shades which are otherwise very difficult to obtain.
- Tin brightens colours.
- Tannic acid, used traditionally with other mordants, will add brilliancy.
- Chrome is good for obtaining yellows.
- Oxalic acid is good for extracting blues from berries.
- Cream of Tartar is not really a mordant but is used to give a lustre to wool.
Mordants are often poisonous, and in the dye-house they should be kept on a high shelf out of the reach of children. Always use protective clothing when working with mordants and avoid breathing the fumes.
The mordant can be added before, during or after the dyeing stage, although most recipes call for mordanting to take place prior to dyeing. It is best to follow the instructions given in the recipe being used or experiment on a sample before carrying out the final dyeing. Later in this brief we will explain how the mordant is mixed and used as part of the dyeing process.
These chemical mordants are usually obtained from specialist suppliers or from chemists. Where this is prohibitive, due to location or cost, natural mordants can be used. There are a number of plants and minerals which will yield a suitable mordant, but their availability will be dependent upon your surroundings. Some common substitutes for a selection of mordants are listed below.
- Some plants, such as mosses and tea, contain a small amount of aluminium. This can be used as a substitute to alum. It is difficult to know, however, how much aluminium will be present and experimentation may be necessary.
- Iron water can be used as a substitute to ferrous sulphate. This can be made simply by adding some rusty nails and a cupful of vinegar to a bucket-full of water and allowing the mixture to sit for a couple of weeks.
- Oak galls or sumach leaves can be used a substitute to tannic acid.
- Rhubarb leaves contain oxalic acid.
Natural dyestuffs
Dyestuffs and dyeing are as old as textiles themselves. Nature provides a wealth of plants which will yield their colour for the purpose of dyeing, many having been used since antiquity. In this section we will look at some of these naturally occurring dyes, their source and the colours they produce. Later in the brief we will look at the application of the dyes to textiles.
Almost any organic material will produce a colour when boiled in a dye-bath, but only certain plants will yield a colour that will act as a dye. The plants given in Table 1 are a selection of plants that have stood the test of time, and are used widely and traditionally by natural dyers. Natural dyes fall into the following categories:
- Leaves and stems
* Twigs and prunings
* Flower heads
* Barks
* Roots
* Outer skins, hulls and husks
* Heartwoods and wood shavings
* Berries and seeds
* Lichens
* Insect dyes
|
Common Name |
Latin Name |
Parts Used |
General Colour Guide |
Suggested Mordant |
|
Alder |
Alnus spp |
Bark |
Yellow/brown/black |
Alum, iron. Copper sulphate |
|
Alkanet |
Anchusa tinctoria |
Root |
Grey |
Alum, cream of tartar |
|
Apple |
Malus spp |
Bark |
Yellow |
Alum |
|
Blackberry |
Rubus spp |
Berries, young shoots |
Pink, Purple |
Alum, tin |
|
Betel nut |
Areca catechu |
Nut |
Deep pink | |
|
Blackwillow |
Salix negra |
Bark |
Red, brown |
Iron |
|
Bloodroot |
Sanguinaria canadensis |
Roots |
Red |
Alum, tin |
|
Buckthorn |
Rhammus cathartica |
Twigs, berries, bark |
Yellow, brown |
Alum, cream of tartar, tin, iron |
|
Cherry (wild) |
Prunus spp |
Bark |
Pink, yellow, brown |
Alum |
|
Dahlia |
Dahlia spp |
Petals |
Yellow bronze |
Alum |
|
Dog’s mercury |
Mercurialis perennis |
Whole plant |
Yellow |
Alum |
|
Dyer’s broom |
Genista tinctoria |
Flowering tops |
Yellow |
Alum |
|
Elder |
Sambucus negra |
Leaves, berreis, bark |
Yellow, grey |
Iron, alum |
|
Eucalyptus |
Eucalyptus |
Leaves |
Deep gold, grey | |
|
Fustic |
Chloropho-ria tinctoria |
Wood shavings |
Yellow | |
|
Groundnut |
Arachis hypogea |
Kernel skins |
Purple, brown, pink |
Copper sulphate, alum |
|
Henna |
Lawsonia inermis |
Leaves |
Gold | |
|
Hypogymnia lichen |
Hypogymnia psychodes |
Whole lichen |
Gold, brown | |
|
Indigo |
Indigofera |
Leaves |
Blue |
Not required |
|
Ivy |
Hedera helix |
Berries |
Yellow, green |
Alum, tin |
|
Madder |
Rubia tinctora |
Whole plant |
Orange, red |
Alum, tin |
|
Maple |
Acer spp |
Bark |
Tan |
Copper sulphate |
|
Marigold |
Calendual spp |
Whole plant, flower heads |
Yellow |
Alum |
|
Nettles |
Urtica dioica |
Leaves |
Beige, yellowy greens |
Alum, copper |
|
Onion |
Allium cepa |
Skins |
Yellow, orange |
Alum |
|
Oak |
Quercus spp |
Inner bark |
Gold, brown |
Alum |
|
Ochrolech-ina lichen |
Ochrolech-ina parella |
Whole lichen |
Orange, red (when fermanted in urine then boiled) |
Alum |
|
Privet |
Ligustrum vulgare |
Leaves, berries |
Yellow, green, red, purple |
Alum, tin |
|
Ragwort |
Senecio |
Flowers |
Deep yellow | |
|
Safflower |
Carthamus tinctoria |
Petals |
Yellow, red |
Alum |
|
Sloe-Blackthorn |
Prunus spinosa |
Sloe berries, bark |
Red, pink, brown |
Alum |
|
Tea |
Camelia sinensis |
Leaves |
Beige | |
|
Turmeric |
Circuma longa |
Root |
Yellow | |
|
Wild mangosteen |
Diospyros peregrina |
Fruit |
Grey, pink | |
|
Weld (wild mignonette) |
Reseda luteula |
Whole plant |
Olive green |
Alum, cream of tartar |
|
Woad |
Isatis tinctoria |
Whole plant |
Blue |
Lime |
Table 1. A list of plants commonly used for preparing dyes.
The choice of mordant for a particular plant is dependant upon the material with which it will be used. It is necessary to check a recipe before using a plant, or one can experiment to see what effect a mordant has for a particular application.
It is recommended that plants be grown specifically for the purpose of dyeing. Harvesting plants from the wild on a non-sustainable basis can endanger the survival of the plant. Many lichens are registered as protected organisms and it is illegal to gather them from the wild. One source of lichen is from timber mills where logged trees are being processed, but ask first!
Testing dyes
It is always useful and interesting to test the dye which is to be used on a sample of the yarn or fabric to be dyed. The outcome will depend on the fabric, the mordant that has been used and dye that has have been chosen. Testing is best carried out on a series of marked (for identification) samples, which have been mordanted with a number of different mordants. Tests can be carried out for light, water and washing fastness using simple standard test methods. Box 1 shows a simple test for washing fastness. Similar tests exists for water and light fastness (and are given in detail in the same book).
Box 1
|
Test method for fastness to washing To test for fastness follow these steps:
|
Source: Dyeing and printing: a handbook, ITDG Publishing
Processing of the plant can take one of many forms, but usually takes the form of soaking or boiling the plant to extract the dye. Some plants, such as indigo, need special preparation for use. Some plants will need boiling to extract their dye while others can merely be soaked for extended periods. Detailed instructions for processing of a wide variety of plants can be found in some of the texts given in the reference chapter at the end of this document.
The process of dyeing
Application of the Dye
Dyeing can be carried out at any of the following stages in the textile manufacturing stage:
- The fibres can be dyed before they are spun. Fibre dyeing provides a deep penetration of the dye into the fibre, giving even colour and excellent colour-fastness.
- The yarn can be dyed after spinning but before the product is woven or otherwise fabricated. This is called package dyeing.
- Before the fabric is finished, it can be dyed in lengths (piece dyeing).This process allows manufacturers the opportunity to produce fabrics in their natural colours, and then dye them to order.
- In cross-dyeing, fabrics of two or more fibres can be dyed so that each fibre accepts a different dyestuff and becomes a different colour, through the use of appropriate dyestuffs for each fibre.
It is essential for the correct identification of the fibre or other fabric to be made before dyeing commences.
Methods of dyeing
There are a number of methods of applying dye to a fabric. Although the most common method used for applying natural dyes is the vat method, there are techniques which have been developed to allow patterns to be incorporated during the dying process. It is worth bearing in mind that using natural dyes is a complex art and the skills required for using natural dyes are learned over many years. Don’t be put off if you don’t get the desired results at the first attempt!
Vat Dyeing
In the simplest form of dyeing a textile material is immersed in dye and gradually brought to the boil. Alternatively the fibre is allowed to sit and soak for several hours or days. During this period, agitation is necessary to allow full penetration of the textile by the dyestuff. Depending on the type of fabric and dyestuff used, certain salts or acids may be added to assist absorption of the dye.
The principal difficulty in dyeing mixed yarns and fabrics is to achieve the same colour in both fibres. Cotton fibres may, for instance, absorb dyes rapidly, while the wool fibres will have to be boiled over an extended period to reach the same depth of shade. This could lead to significant damage to the material. In this case a chemical compound would need to be used to restrain the rate at which the cotton fibre takes up the dyestuff.
The amount of dyestuff which is used is usually given in the recipe. It is usually quoted as a percentage weight of the fabric to be dyed. Box 2 demonstrates a typical, simple recipe for dyeing using natural dyestuff, in this case onion skins.
Box 2
|
Recipe for dyeing wool with onion skins Fabric: applicable to wool or other animal (protein) fibres. You will need:
Weigh the wool. All weights given are relative to the dry weight of the wool. Skeins of wool are tied loosely in several places to prevent tangling. In this case the recipe calls for 30% dyestuff i.e. the weight of the dyestuff is 30% that of the fabric to be dyed. The wool should be scoured. This means getting the wool completely clean. For this the wool is soaked overnight in a liquid detergent solution. Rinse the wool well and gently squeeze out the excess water. Use lukewarm water and avoid sudden changes in the temperature of the water which cause the wool to felt or mat. Next the skein will be mordanted. Dissolve the alum and cream of tartar in a little hot water and then add this solution to cool water in the mordant pan. Immerse the wetted yarn and then place the pan on the heat source. Slowly raise the temperature to 82oC (180oF) and simmer for 45 minutes. Leave to cool, then remove the wool and rinse well. To prepare the dyebath, place the onion skins in the dyepan and cover them with water. Slowly heat the dyebath to boiling point. Simmer for about 45 minutes by which time all the colour should have been extracted from the onion skins. Remove from the heat, allow to cool and then strain of the liquid form the skins. The dyeing process is then carried out. The mordanted, thoroughly wetted fabric is placed into the now cool dyebath. Replace the heat under the dyebath, bring the temperature up to boiling point and then immediately reduce the heat to 82oC (180oF) and simmer for 45 minutes or until the wool is the required colour. Remember that wool is darker when wet than when dry. Remove the wool from the dyebath if no further uptake of dye is required, or allow the fabric to cool with the liquid in the dyebath. Do not cool quickly with cold water. When the skein of wool is cool, rinse it thoroughly in several changes of water until the water is clear, then wash the skein of wool in soapy water, rinse and allow to dry. *Ordinary tap water is normally suitable for dyeing. If ‘soft’ water is called for then rain water can be used. A plentiful supply of fresh water is always required when dyeing. |
Source: The Craft of Natural Dyeing, Jenny Dean
Batik
Batik is a starch resist-dyeing process, developed on the Island of Java in modern-day Indonesia. Colour is prevented from reaching certain areas of a fabric by covering these areas with molten wax. The fabric is starched prior to the design being drawn upon it. The wax is applied with a type of cup with a fine pouring spout, usually made of copper. The technique has been developed to a high art form in Indonesia from where it is exported to many parts of the world. Batik paintings, as well as sarongs and lengths of fabric, are produced. When the fabric is dyed, all waxed areas resist the dyestuff. The wax is then removed by placing the fabric in boiling water. For patterns with many colours the same procedure is repeated until the full design is completed.
Tie-dyeing
Tie-dyeing is another popular artisanal dyeing technique. In this resist-dyeing process, waxed thread is tightly tied around the areas chosen to resist the coloured dyestuff, and the fabric is dipped into the dye. The waxed thread is then removed and the fabric dried. This process can be repeated for each colour to be added.
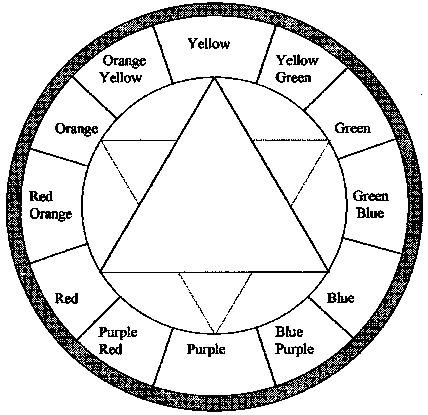
Obtaining unusual colours
Colours other than those obtained by simply using a single dye, can be obtained by mixing dyes or dyeing a fabric more than once in different dyebaths. The colour triangle on the next page is a useful tool in determining the colours needed to produce a required shade.
References and further reading
This Howtopedia entry was derived from the Practical Action Technical Brief Natural Dyeing of Textiles.
To look at the original document follow this link: http://www.practicalaction.org/?id=technical_briefs_manufacturing
Foulds, John, Dyeing and printing: a handbook, ITDG Publishing, 1989. The text and line drawings describe chemical dyeing and printing techniques as they apply to small-scale operations. 128pp.
Sayadda R. Ghuznavi, Rangeen - Natural dyes of Bangladesh, Vegetable Dye Research and Development Society, Bangladesh, 1987. This interesting book gives listings of indigenous Bangladeshi plants as well as recipes for their use.
Dalby, Gill and Dean, Jenny, Natural Dyes in Luapula Province (Zambia): Evaluation of Potential for Production, Use and Export. Working Paper 22, Development Technology Unit, University of Warwick, Coventry CV4 7AL, UK. 1988.
Dean, Jenny: The Craft Of Natural Dyeing, Search Press, 1994 This guide tells how to grow and find, harvest, and use all NON-TOXIC dyes in nature. It is excellent for children. She lists dyestuffs that provide a full spectrum of colours and explains how to test plant dyestuffs for colour potential. 64 pgs, 30 colour photos, 16 illustrated charts, paperback.
Cowan, Wavell: Operating A Business In The Small Business Space. A must for anyone who contemplates starting a small business. Xeroxed, spiral bound, non-profit 67 pp.
McRae, Bobbie: Colors From Nature: Growing, Collecting, and Using Natural Dyes How to grow dye plants, recognise and collect wild plants, and even find dyes in the produce department of the grocery store. Step-by-step instructions for over a dozen naturally dyed crafts projects. 168 pp.
</div>
Useful addresses
Practical Action
The Schumacher Centre for Technology & Development, Bourton on Dunsmore, RUGBY, CV23 9QZ, United Kingdom.
Tel.: +44 (0) 1926 634400, Fax: +44 (0) 1926 634401
e-mail:practicalaction@practicalaction.org.uk
web:www.practicalaction.org

Earth Guild, 33 Haywood Street Asheville NC 28801,
USA
Tel: +1 800 327 8448, Fax: +1 (704) 255 8593
Suppliers of natural dyes and dyeing equipment.
Vegetable Dye Research and Development Society,
P.O.Box 268, Dhaka, Bangladesh.
Carry out R&D and publish books on Natural Dyeing
The Crafts Council,
1 Oxenden Street, London SW1Y 4AT. United Kingdom
Tel: +44 (0)20 7930 4811
Khadi and Village Industries Commission,
Irla, Vile Parle, Bombay 400056, India
Society of Dyers and Colourists,
PO Box 244, Perkin House, 82 Graton Road, Bradford BD1 2JB, United Kingdom
Produce a Colour Index of all known natural and manufactured dyes, but it is very expensive.
Useful internet addresses
http://www.earthguild.com/products/Dyes/dye.htm Homepage of Earth Guild (see addresses section above).
http://www.slonet.org/~crowland/index.html Carol Todd’s Natural Dyeing Homepage. Sells books and electronic database of plants and natural dyes.
http://www.hillcreekfiberstudio.com/Workshops.html Hillcreek Fibre Studio. Runs workshops on weaving and natural dyeing. Based in the USA.
There are many recipes for natural dyeing given on the Internet. Enter a search on ‘Natural dyeing’ and this will yield a wealth of recipes, suggestions and ideas for the novice (and experienced) dyer.
Related articles
- How to Dye Fabric / Textile with Natural Colors
- What to Do with Fabric
- How to Recycle Fabric
Support the work of howtopedia, help us to continue to write and translate more practical articles on simple technologies!
<paypal />
Categories
How to Recycle Fabric
The obvious answer to the recycling of fabric is to make it into other things.
Anyone who sews even just occasionally will know that there is a certain amount of "left-over" scraps that just aren't good for much of anything given their size. That's how Patchwork bed covers was invented
Second-hand shops:
"reduce, re-use, recycle"
Donate clothings you do not use anymore and visit second-hand shops once in a while where you might find the piece you need.
Felting/fulling an old wool sweater in the wash then cutting it up to make slippers, bags and mittens? Any sweater that is mostly animal fiber will felt in hot water. The felting is the result of harsh mouvements of the wool in hot water, as wool fibers open and interwine. If you use a washing machine throw in a couple pair of jeans or tennis balls to help the fabric felt up evenly.
knit and crochet.
With some patience and planning, you can deconstruct old knits - sweaters, skirts, etc - and re-use the yarn to make other items. Be careful to choose a knit that does not have serged seams; they indicate that the garment was probably cut from a large fabric and you will end up with lots of little strings and very little usable yarn.
Don't be afraid to make old clothes into new clothes. Unless sewing is very new to you, it is a great way to freshen up the wardrobe. Embellishing clothing has become a popular trend. There are hundreds of articles online as well as books and magazines that can give you inspiration.
- Small Business
- Agriculture
- Fruits
- Ideas
- Pollution
- Products
- Recycling
- Water
- Easy to Medium
- Global Technology
- Arid Climate
- Forest Environment
- Global
- Mediterranean Climate
- Monsoon Climate
- Montaneous Environment
- Coastal Area
- Lakes and Rivers
- Rural Environment
- Temperate Climate
- Tropical Climate
- Urban Environment
- Less than 10 US$
- Ashes
- Plastic container
- Seeds
- Tea
- Wood
- Wool
- Fly Ash
- One Person and more
- Household
- Village
- Requested translation to Spanish
- Requested translation to French
- Requested translation to Arabic
- Requested translation to Hindi
- Stub