Quality Control In Food Processing Businesses
Contents
Short Description
- Problem: Principals of Quality Control in Food Processing
- Difficulty: small to high
Introduction
Quality control (QC) is not an optional extra in food processing, neither is it something that is only done by large manufacturers. It is an essential component of any food processing business. The purposes of quality control are:
- To protect the customers from dangers (e.g. contaminated foods) and ensure that they get the weight and quality of food that they pay for.
- To protect the business from cheating by suppliers, damage to equipment (e.g. stones in raw materials) and false accusations by middlemen, customers or suppliers.
- To be sure that food laws operating in a country are complied with.
Quality control need not be time-consuming or expensive and the results of quality control tests should help save money in the long run. In general, the quality control procedures used should be as simple as possible and only give the required amount of information (too little information means the test has not done its job, too much information and management decisions may be delayed or confused).
Quality control is used to predict and control the quality of processed foods. It is no use producing a food, testing it to find the quality and then trying to find a buyer for that particular batch of food. Quality control is used to predict the quality of the processed food and then control the process so that the expected quality is achieved for every batch. This means that quality specifications must be written and agreed with suppliers or sellers and control points must be identified in the process.
Quality specifications
The quality of foods or ingredients can be measured in different ways but one popular method is to describe 'quality attributes', see Table 1. A specification can then be written and agreed with the supplier or seller, which lists the quality attributes that are required in a food. An example of a quality specification for tomatoes intended for processing into a paste or leather is shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Quality attributes for tomatoes
|
Attribute |
Accept |
Reject |
|
Colour |
Orange/red |
More than 10% green |
|
Size |
Any |
- |
|
Shape |
Any |
- |
|
Damage |
|
|
|
Hardness |
Soft to oversoft |
More than 10% hard |
A number of points arise from such a specification:
• A representative sample of the food must be tested to make sure the whole batch meets the specification (for small batches it might be possible to examine every item). The size of sample needed for testing can be calculated, but this is fairly complex and usually unnecessary for a small-scale business.
• The percentage of substandard items which cause a batch to fail the test can be increased or decreased depending on how reliable the supplier is or how important the particular attribute is to the seller/manufacturer.
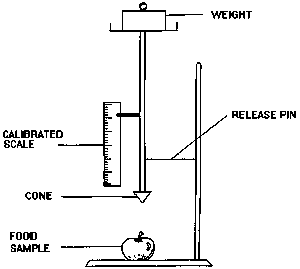
• Some attributes may need to be tested using equipment to avoid arguments over interpretation. In Figure 1 the hardness could be tested with a simple 'penetrometer' to define what is 'hard' and what is 'soft'.
The size and shape of the tomatoes is not important because they are to be crushed to a pulp. In other examples (eg fruit for bottling) the size might be important. The ripeness and flavour of the tomatoes (assessed by colour and hardness) and damage caused by poor storage and handling are very important and the specification concentrates on these. Each specification takes account of the intended use of the products and the likely important faults that could be expected.
|
Quality attribute |
Example |
|
Quantitative |
6 |
|
Hidden | |
|
Harmful substances |
Aflatoxin in groundnuts |
|
Microbiological |
Number of bacteria in a food |
|
Nutritive value |
Vitamin content of a food |
|
Additives |
Artificial flavours, thickeners etc |
|
Sensory | |
|
Colour |
Ripeness of fruit |
|
Size, shape (appearance) |
Size of chopped food, particle size of flour |
|
Thickness or texture |
Juice consistency, toughness of meat |
|
Taste |
Saltiness, sweetness, sourness and bitterness |
|
Flavour |
Characteristic flavour of tomato |
Control points
In every food process there are particular stages which affect the quality of the final product (eg the amount of heating given to pasteurised juices affects the colour, flavour and storage life or in sausage the amount and type of grinding affects the texture of the meat). These stages are identified as control points and quality control checks are made at these points to control the process.
Manufacturers therefore need to identify the control points in their process (using outside technical assistance if necessary) and set up a specification for the operators to use. For example, in jam making the amount of pectin, fruit and sugar should be carefully controlled and weighing of ingredients is a control point (weights of each ingredient specified and each carefully weighed out). Likewise the acidity of the jam, the sugar content after boiling and the temperature of filling are each control points. The mix should be checked for correct acidity, the sugar content checked during boiling using a thermometer or refractometer and the temperature checked before filling using a thermometer.
Checks at the control points can therefore be used to control the process and ensure that each batch of product has a similar quality.
References and further reading
This Howtopedia entry was derived from the Practical Action Technical Brief Quality Control: In Food Processing Businesses.
To look at the original document follow this link: http://www.practicalaction.org/?id=technical_briefs_food_processing
Food Processing Equipment Design Technical Brief Practical Action
Food Processing Building Design Technical Brief Practical Action
Food Poisoning & Its Prevention Technical Brief Practical Action
Quality Assurance for Small-scale Rural Food Industries: FAO Agricultural Series Bulletin 117, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations 1995
Food Hygiene Training: A Guide to its Responsible Management Institute of Food Science and Technology 1992
Making Safe Food: A guide to Safe Food Handling and Packaging for Small-scale Producers ITDG Publishing 1998
Starting a Small Food Processing Enterprise ITDG Publishing 1996
Usefull addresses
Practical Action
The Schumacher Centre for Technology & Development, Bourton on Dunsmore, RUGBY, CV23 9QZ, United Kingdom.
Tel.: +44 (0) 1926 634400, Fax: +44 (0) 1926 634401
e-mail:practicalaction@practicalaction.org.uk
web:www.practicalaction.org

NR International
Central Avenue
Chatham Maritime
Kent
ME4 4TB
United Kingdom
Tel: +44 1634 880088
Fax: +44 1634 880066/77
Email: info@nrint.co.uk
Website: http://www.nrinternational.co.uk/
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
Website: http://www.fao.org/