How to Grow Moringa Trees
Contents
How To Grow Moringa
Short Description
- Problem:
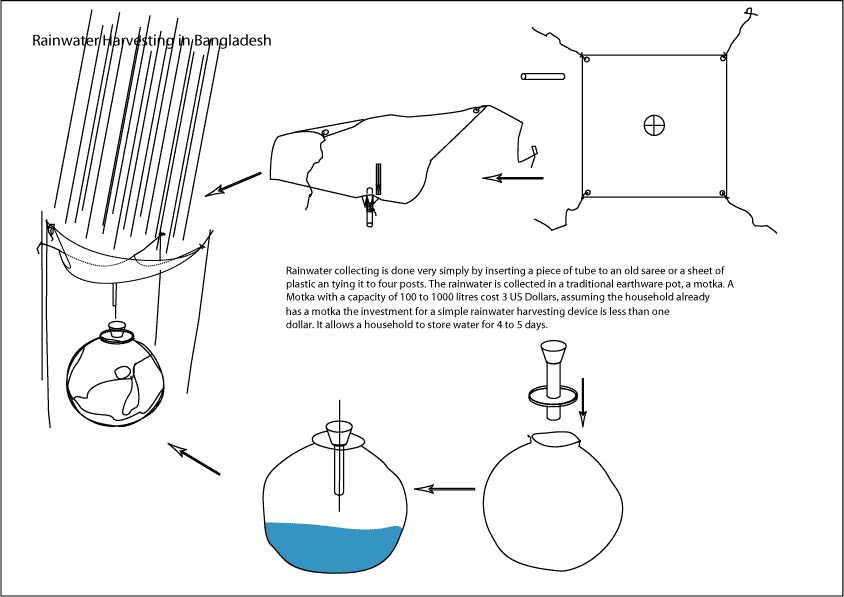
- Idea:
- Difficulty:
- Price Range:
- Material Needed:
- Geographic Area:
- Competencies:
- How Many people?
- How Long does it take?
Moringa trees grow easily from seeds or cuttings. They grow quickly even in poor soil and bloom 8 months after planting.
Where Moringa grows
The Moringa tree grows mainly in semi-arid tropical and sub-tropical areas. It grows best between 25 and 35 C (77 to 95 F), but will tolerate 48 C (118 F) in the shade and can survive a light frost. Altitudes below 600 m (1,970') are optimal, but it has been known to grow at altitudes as high as 1200 m (3940') in the tropics.
In the USA it can only grow outdoors and possibly year-round in places like the southern parts of Florida, Arizona, California and Texas. However, people in cooler climates can grow it indoors, outdoors as an annual, or in greenhouses.
<a title="cutting" name="cutting"></a>To grow from a cutting:
After the trees have stopped producing fruits each year, branches need to be cut off so that fresh growth may take place. These branches are excellent for growing new trees.
- Make a cutting at least 1" (2.5cm) in diameter and at least six feet (1.8m) long.
- Dig a hole 3 ft. (1m) x 3 ft. (1m) and 3 ft. (1m) deep.
- Place cutting in this hole and fill with a mixture of soil, sand and composted manure. Pack firmly around base of the cutting. Form a slight dome or cone shape, sloping down away from the cutting. It is desirable that water not touch the stem of the new tree.
- Water generously, but do not drown the cutting in water.
In India, the custom is to put some cow dung on top of the open end of the cutting. This is an excellent way to protect the cutting from pests.
To grow from seed:
Moringa seeds have no dormancy periods and can be planted as soon as they are mature.
<a title="ground" name="ground"></a>In the ground:
It is best to plant the seeds directly where the tree is intended to grow and not transplant the seedling. The young seedlings are fragile and often cannot survive transplanting. To plant seeds directly in the ground:
- Choose an area with light and sandy soil, not heavy with clay or water-logged.
- Dig holes 1 ft (30 cm) square and 1 ft deep. Back-fill the holes with loose soil. Compost or manure will help the tree grow better, even though Moringa trees can grow in poor soils.
- Plant 3 to 5 seeds in each hole, 2 in. (5 cm) apart. Plant the seeds no deeper than three times the width of the seed (approximately ½ in. or 1.5 cm -- the size of one's thumbnail).
- Keep the soil moist enough so that the top soil will not dry and choke the emerging saplings, but it should not too wet or else the seeds can drown and rot.
- When the saplings are four to six inches tall, keep the healthiest sapling in the ground and remove the rest. Termites and nematodes can kill a young sapling. Take measures to protect saplings from these two dangers.
Note: If the soil is heavy, dig a larger hole of up to 3 ft (90 cm) in diameter and 3 ft deep, and backfill with 1 part sand and 2 parts original soil. Added compost or manure will help.
<a title="plastic" name="plastic"></a>
In Plastic Bags:
When it is not possible to plant directly in the ground, use the following method:
- Fill seedling bags with light soil mixture, i.e. 3 parts soil to 1 part sand.
- Plant two or three seeds in each bag, ¼ in. (0.5 cm) deep.
- Keep moist but not too wet. Germination will occur within two weeks.
- Remove extra seedlings, leaving one in each bag.
Seedlings can be transplanted after four to six months when they are 2-3 ft (60-90 cm) high.
<a title="transplanting" name="transplanting"></a>
Transplanting:
The ground where the trees are to be planted should be light and sandy, not heavy with clay or water-logged.
Dig a hole 1 ft (30 cm) square and 1 ft deep. Backfill with loose soil. Adding compost or manure will help the trees grow better.
- Water the planting holes one day before transplanting the seedlings.
- Plant seedlings in the late afternoon to avoid the hot sun the first day.
- Make a hole in the pit to accept all soil in the bag. Carefully cut open the sack and place the seedling in the planting hole. Be careful to keep the soil around the seedling's roots intact.
- Pack soil around the seedling base.
- Water only lightly for the first few days.
If the seedlings fall over, tie them to a stick for support. Protect young saplings from termites and nematodes.
helptopic on images: [1]
Contacts
They are the real people behind the technologies. That is to say You. It is important not to leave the technologies "alone", BUT don't give the contact information of someone you don't know and who didn't give his or her permission to do so.
Links
Don't give too many links, try to give quality, not quantity. Choose them carefully as being real reference links for the technology you are presenting.
Bibliography
The same as for the links. If you have a very good bibliography, though, don't hesitate to create a separate article, specified as a bibliography, with links and books.
Related articles
Mention here the other howtopedia articles that relate to the subject.
Name them exactly the same as the original title so that redirection functions.
And last but not least, link your article to it's translation in another language: [[fr:Modèle]] this will appear in the left side bar.
Categories
Mention the category, that is to say one or more themes for which this article is relevant, so that it can be recognized in these categories, and quickly found by users. Write them this way [[category:Example]]
- Stub
- Agriculture
- Urban Agriculture
- Biogas
- Commercial
- Communication
- Community
- Composting
- Computer
- Construction
- Cooking
- Cooling
- Crops
- Crisis Management
- Energy
- Education
- Equipment Design
- Fertilizer
- Food Poisoning and its Prevention
- Food Processing
- Forest
- Fruits
- Health
- Heating
- Hygiene
- Ideas
- Insects
- Informatics
- Mechanics
- Pest control
- Pollution
- Prevention
- Products
- Pumps
- Recycling
- Resource Management
- Sanitation
- Small Business
- Soil
- Run-Off
- Transportation
- Tree
- Vegetables
- Waste
- Water
- Water harvesting
- Water purification
- Irrigation
- Sun
- Wind
- Sea
- Fishing
- Biodiversity
- Dangerous
- Difficult
- High Technology
- Medium
- Easy to Medium
- Easy
- Global Technology
- Local Technology
- Arid Climate
- Forest Environment
- Global
- Mediterranean Climate
- Monsoon Climate
- Montaneous Environment
- Coastal Area
- Lakes and Rivers
- Rural Environment
- Temperate Climate
- Tropical Climate
- Urban Environment
- Between 50 and 200 US$
- Less than 10 US$
- Less than 50 US$
- More than 200 US$
- Ashes
- Banana
- Bricks
- Cardboard
- Clay
- Cement
- Coal
- Charcoal
- Chillies
- Coffee
- Compost
- Concrete
- Cow dung
- Garlic
- Glass
- Kaolin
- Lime
- Manure
- Mobile Phone
- Oil
- Onions
- Paper
- Plastic container
- Pozzolanas
- Salt
- Sand
- Sawdust
- Seeds
- Seedlings
- Straw
- Tea
- Termites
- Tourism
- Tyres
- Vetiver
- Wood
- Wool
- Worms
- Fly Ash
- One Person and more
- More than 5 Persons
- One Person
- Up to 5 Persons
- Household
- Village
- Neighbourhood
- School
- Application
- Principles
- Administration
- Howtopedia requested articles
- Howtopedia requested drawings
- Howtopedia requested images
- Pages listed for deletion
- Permanently protected
- Requested translation